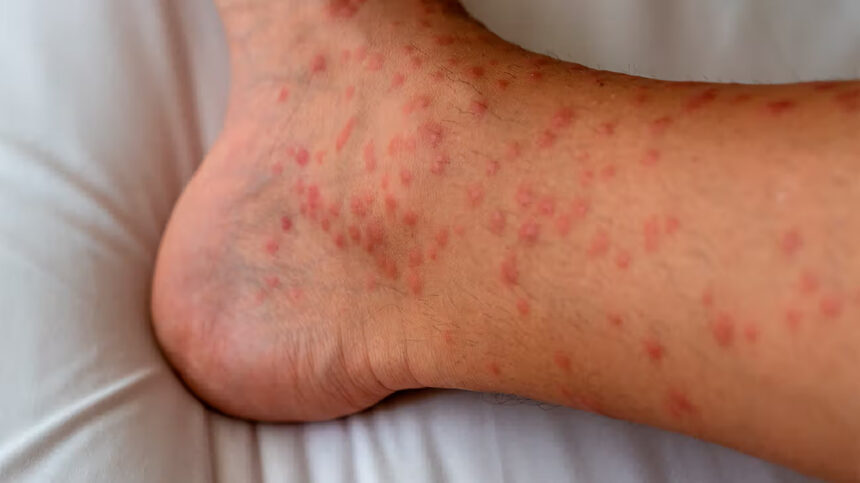
Papules Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the characteristic features of eczema is the appearance of papules, which are small, raised bumps on the skin. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the relationship between papules and eczema, delving into their causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What Are Papules Eczema?
Papules are a common manifestation of eczema, appearing as small, raised bumps on the skin’s surface. These bumps are typically less than 1 centimeter in diameter and can be red, pink, or skin-colored. When eczema flares up, papules often develop alongside other symptoms such as itching, redness, and dryness.
Key Characteristics of Papules Eczema:
- Size: Usually smaller than 1 cm in diameter
- Texture: Raised and firm to the touch
- Color: Can be red, pink, or match the skin tone
- Distribution: Often appear in clusters or patches
- Sensation: Frequently itchy and may be tender
Causes of Papules Eczema
Understanding the underlying causes of papules in eczema is crucial for effective management and treatment. Moreover, several factors contribute to their formation:
- Inflammation: Eczema is characterized by chronic inflammation of the skin. This inflammatory response can lead to the formation of papules as the body attempts to protect and heal affected areas.
- Immune System Dysfunction: People with eczema often have an overactive immune system, which can trigger excessive reactions to environmental irritants and allergens, resulting in papule formation.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: Eczema compromises the skin’s natural barrier function, making it more susceptible to irritants and allergens that can provoke papule development.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain substances or conditions can exacerbate eczema and lead to papule formation. Common triggers include:
- Harsh soaps and detergents
- Extreme temperatures
- Low humidity
- Certain fabrics (e.g., wool or synthetic materials)
- Stress
- Sweat
- Genetic Factors: A family history of eczema or other atopic conditions can increase the likelihood of developing papules and other atopic dermatitis symptoms.
- Microbial Colonization: The skin of individuals with atopic dermatitis is often colonized by bacteria, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, which can contribute to inflammation and papule formation.
Diagnosis of Papules Eczema
Dermatologists typically diagnose papules eczema through a combination of visual examination and patient history. In some cases, additional tests may be necessary:
- Skin Examination: A dermatologist will carefully inspect the affected areas, looking for characteristic signs of eczema, including papules.
- Patient History: Information about symptoms, triggers, and family history of atopic conditions helps in making an accurate diagnosis.
- Patch Testing: This may be performed to identify specific allergens that could be triggering atopic dermatitis flares and papule formation.
- Skin Biopsy: In rare cases, a small sample of skin may be taken to rule out other conditions with similar appearances.
Treatment Options for Papules Eczema
Effectively managing papules eczema often involves a multi-faceted approach; combining topical treatments, systemic therapies, and lifestyle modifications:
Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroid Creams: These anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce itching, redness, and papule formation. A healthcare professional should direct the use of these to avoid side effects.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Topical medications like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus can help manage eczema symptoms, including papules, without the side effects associated with long-term steroid use.
- Moisturizers: Regular use of medicated moisturizing cream helps maintain skin hydration, strengthens the skin barrier, and may prevent papule formation.
- Topical Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to address both the infection and associated papules.
Systemic Therapies
- Oral Antihistamines: These can help reduce itching, which may indirectly decrease papule formation by minimizing scratching.
- Systemic Corticosteroids: In severe cases, oral or injectable corticosteroids may be prescribed for short-term use to control extensive papule outbreaks.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be used in severe, resistant cases to modulate the immune response and reduce papule formation.
Light Therapy
Phototherapy, particularly narrow-band UVB treatment, can be effective in managing eczema symptoms, including papules, by reducing inflammation and itching.
Prevention Strategies for Atopic Dermatitis
Preventing papules in eczema focuses on managing the condition overall and avoiding triggers:
- Skin Care Routine: Establish a consistent skincare regimen that includes gentle cleansing and regular moisturizing to maintain skin barrier function.
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: Keep a diary to track potential triggers and work to minimize exposure to known irritants and allergens.
- Manage Stress: Since stress can exacerbate atopic dermatitis, incorporate stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine.
- Choose Appropriate Clothing: Opt for soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoid rough materials that can irritate the skin.
- Control Environment: Use a humidifier in dry climates, maintain moderate room temperatures, and keep living spaces clean to reduce exposure to dust and allergens.
- Diet Considerations: While the link between diet and atopic dermatitis is not fully understood, some individuals may benefit from identifying and avoiding food triggers.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain overall skin health and hydration.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While you can manage many cases of papules in eczema at home, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if:
- Papules become increasingly numerous or widespread
- There are signs of infection (increased redness, warmth, pain, or pus)
- Eczema symptoms significantly impact the quality of life
- Over-the-counter treatments are ineffective
- New or unusual symptoms develop
Conclusion
Papules are a common and often challenging aspect of eczema. By understanding their causes, exploring various treatment options, and implementing effective prevention strategies, individuals with atopic dermatitis can better manage their condition and reduce the occurrence of papules. Remember that atopic dermatitis management is highly individual, and what works for one person may not work for another. Working closely with a dermatologist or healthcare provider can help develop a personalized treatment plan to effectively address papules and other atopic dermatitis symptoms, improving overall skin health and quality of life.