Introduction
A complex neurodevelopmental disorder known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is marked by difficulties with social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviours. As awareness of autism has grown, so too has the understanding and development of therapeutic approaches designed to support individuals with ASD. This comprehensive guide explores the various types of autism therapies, their effectiveness, and how they can be tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual.
Definition
Autism treatment includes a range of techniques designed to help people on the autism spectrum with their behaviour, social skills, and communication. The goals of therapies including occupational therapy, speech therapy, sensory integration therapy, and applied behaviour analysis (ABA) are to improve quality of life by addressing particular problems. Tailored plans frequently incorporate organized exercises and assistance to enable people with autism to flourish in everyday life and social situations.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Understanding the complex nature of autism is essential before beginning treatment. Since ASD is a spectrum condition, its effects vary throughout individuals. Some people with autism may have significant intellectual disabilities, while others may be highly intelligent but struggle with social interactions. Common symptoms of autism include difficulties with communication, challenges in understanding social cues, repetitive behaviors, and specific interests or preoccupations.
The Goals of Autism Therapy
The primary goal of autism therapy is to enhance the individual’s quality of life by improving communication skills, social interactions, and behavioral regulation. The goal of therapy is to assist clients in acquiring the abilities necessary to function in daily life, promote independence, and take an active role in their communities. It is crucial to recognize that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to autism therapy; each individual’s needs and strengths must be considered to create an effective treatment plan.
Types of Autism Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is one of the most widely recognized and utilized therapies for autism. ABA is a science-based method that emphasises using positive reinforcement to comprehend behaviour and change it. It entails decreasing undesirable behaviours while increasing desired ones and dissecting intricate behaviours into smaller, more manageable steps.
Key Components of ABA:
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): A structured teaching method that uses one-on-one sessions to teach specific skills in a step-by-step manner.
- Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT): A play-based approach that targets key developmental areas such as motivation and response to multiple cues.
- Natural Environment Teaching (NET): Integrates learning opportunities into natural settings and everyday activities.
ABA has been shown to be effective in improving communication, social skills, and adaptive behaviors in individuals with autism. However, it’s crucial to make sure that ABA programmes are customised to each person’s needs and run by qualified experts.
Speech and Language Therapy
Many individuals with autism experience challenges with communication, making speech and language therapy a crucial component of their treatment plan. Speech therapists work with individuals to improve their verbal and nonverbal communication skills, helping them to express their needs, understand others, and engage in social interactions.
Techniques Used in Speech and Language Therapy:
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC): Utilizes tools and devices, such as picture boards and speech-generating devices, to support communication.
- Social Skills Training: Focuses on teaching individuals how to interpret social cues, engage in conversations, and develop relationships.
- Language Intervention Activities: Involves interactive exercises to build vocabulary, grammar, and comprehension skills.
Speech and language therapy is highly individualized and can significantly enhance an individual’s ability to communicate and interact with others.
Occupational Therapy (OT)
Occupational therapy aims to help individuals with autism develop the skills needed for daily living and independent functioning. Occupational therapists work on a range of areas, including fine motor skills, sensory processing, self-care, and play skills.
Areas Addressed in Occupational Therapy:
- Sensory Integration: Helps individuals manage sensory sensitivities and improve their ability to process sensory information.
- Fine Motor Skills: Focuses on developing hand-eye coordination and dexterity needed for tasks like writing and dressing.
- Self-Care Skills: Teaches essential skills such as grooming, eating, and toileting.
Occupational therapy can significantly increase a person’s independence overall and their capacity to carry out daily tasks.
Social Skills Training
Social skills training is designed to help individuals with autism navigate social interactions and build meaningful relationships. This therapy often involves structured group activities, role-playing, and direct instruction on social norms and behaviors.
Components of Social Skills Training:
- Peer Interaction: Encourages interactions with peers to practice and reinforce social skills in a naturalistic setting.
- Role-Playing: Allows individuals to rehearse social scenarios and develop appropriate responses.
- Social Stories: Uses narratives to explain social situations and expected behaviors.
By enhancing social skills, this therapy helps individuals with autism develop confidence and improve their ability to form connections with others.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that addresses the thoughts and behaviors that contribute to emotional and behavioral challenges. While therapists traditionally used CBT to treat conditions like anxiety and depression, they have adapted the therapy to support individuals with autism, especially those who have co-occurring mental health conditions.
Key Aspects of CBT for Autism:
- Cognitive Restructuring: Helps individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs.
- Behavioral Interventions: Focuses on changing problematic behaviors through reinforcement and skill-building.
- Emotional Regulation: Teaches strategies for managing emotions and reducing anxiety.
CBT can be particularly beneficial for individuals with autism who experience anxiety, obsessive-compulsive behaviors, or other emotional difficulties.
Tailoring Therapy to the Individual
It is essential to customise therapeutic techniques to the unique requirements, strengths, and preferences of each individual due to the heterogeneous nature of autism. A multidisciplinary team can conduct an extensive assessment to find the best therapies and develop a customized treatment plan. This plan should be flexible and adaptable, allowing for adjustments as the individual’s needs and goals evolve.
The Role of Family and Caregivers
In order for autism therapy to be successful, family members and carers are essential. Their involvement and support can enhance the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions and provide a consistent and nurturing environment for the individual. Family training and education programs can equip caregivers with the skills and knowledge needed to support their loved one’s development and well-being.
Emerging Therapies and Future Directions
Researchers are continually exploring new approaches and technologies in the field of autism therapy, as they work towards ongoing research progress. Emerging therapies such as animal-assisted therapy, virtual reality interventions, and neurofeedback show promise in supporting individuals with autism. Additionally, advancements in genetics and neuroscience may lead to more targeted and personalized treatment options in the future.
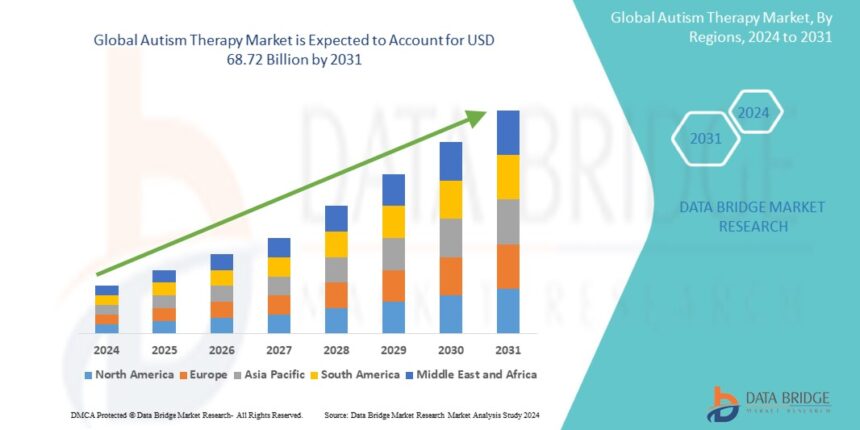
Growth Rate of Autism Therapy Market
The market for autism therapy was estimated to be worth USD 2.19 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.60% from 2024 to 2031, when it is expected to reach USD 68.72 billion.
To read more click here:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-autism-therapy-market
Conclusion
Understanding and supporting individuals with autism through therapy requires a comprehensive and individualized approach. By combining various therapeutic methods and involving family and caregivers, we can help individuals with autism reach their full potential and lead fulfilling lives. As research continues to advance, the future of autism therapy holds exciting possibilities for even more effective and personalized interventions.