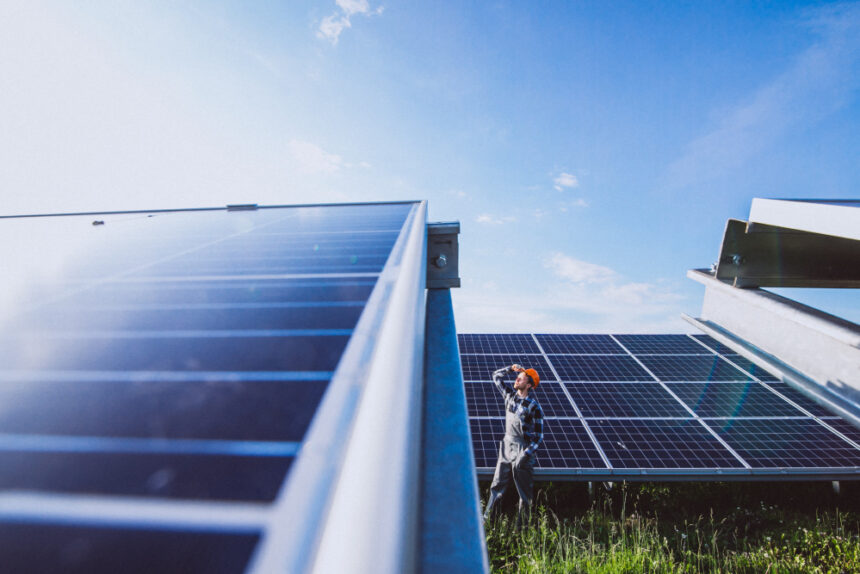
In the arid and sun-soaked landscape of the UAE, where temperatures often soar above 40°C, the potential for harnessing solar energy is immense. With an ever-increasing focus on sustainable development, solar panels have emerged as a pivotal solution in the quest for clean and efficient energy. This blog explores the transformative impact of solar panels in UAE, highlighting their benefits, current applications, and prospects.
1. The Rise of Solar Energy in the UAE
The UAE’s commitment to diversifying its energy sources and reducing its carbon footprint has led to a significant emphasis on solar energy. The country’s geographic advantage—abundant sunshine and clear skies—makes it an ideal location for solar panel installations. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells, providing a renewable energy source that reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
1.1. Government Initiatives and Investments
The UAE government has been instrumental in promoting solar energy through various initiatives and investments. Programs like the UAE Energy Strategy 2050 aim to increase the share of clean energy in the national energy mix. The strategy includes ambitious targets for renewable energy, with solar power playing a central role. By investing in solar technology, the UAE is positioning itself as a leader in the global renewable energy sector.
1.2. Technological Advancements
Advancements in solar panel technology have further accelerated the adoption of solar energy in the UAE. Modern solar panels are more efficient, durable, and cost-effective compared to earlier models. Innovations such as bifacial solar panels, which capture sunlight on both sides, and thin-film solar cells, which are lightweight and flexible, have expanded the possibilities for solar energy applications. These advancements contribute to higher energy yields and more versatile installations.
2. Benefits of Solar Panels in the UAE
The integration of solar panels into the UAE’s energy landscape offers numerous benefits, ranging from environmental advantages to economic gains.
2.1. Environmental Impact
One of the primary benefits of solar panels is their contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By generating electricity from sunlight, solar panels produce no air pollution or carbon dioxide emissions. This clean energy source helps mitigate the effects of climate change and supports the UAE’s goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. Additionally, solar panels reduce dependence on non-renewable energy sources, preserving natural resources for future generations.
2.2. Economic Advantages
Solar panels also offer significant economic benefits. The initial investment in solar technology is offset by long-term savings on electricity bills. As solar panels generate their electricity, users can reduce their reliance on grid power and lower their energy costs. Furthermore, the UAE’s favorable climate ensures that solar panels operate at high efficiency, providing substantial returns on investment. The growth of the solar industry also creates job opportunities and stimulates economic activity within the country.
2.3. Energy Independence and Security
Solar panels enhance energy independence by allowing individuals and businesses to generate their electricity. This decentralization of power reduces vulnerability to fluctuations in energy prices and supply disruptions. In the UAE, where energy security is a strategic priority, solar panels contribute to a more resilient and reliable energy infrastructure. By harnessing the sun’s power, the UAE can ensure a stable energy supply and reduce its dependence on imported fossil fuels.
3. Applications of Solar Panels in the UAE
The versatility of solar panels allows for a wide range of applications across different sectors. In the UAE, solar energy is being utilized in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
3.1. Residential Solar Systems
Residential solar systems have become increasingly popular in the UAE, driven by the desire for energy savings and sustainability. Homeowners are installing solar panels on rooftops to generate electricity for their daily needs. These systems often include battery storage solutions, allowing residents to store excess energy for use during periods of low sunlight. With incentives and rebates available, the adoption of residential solar panels is on the rise.
3.2. Commercial Solar Solutions
Businesses in the UAE are also embracing solar energy to reduce operational costs and enhance their environmental credentials. Commercial solar solutions can range from small-scale installations to large solar arrays on building rooftops or open land. By integrating solar panels UAE into their energy strategy, companies can achieve substantial savings on electricity expenses and improve their corporate sustainability profile.
3.3. Industrial and Utility-Scale Projects
On a larger scale, the UAE is investing in industrial and utility-scale solar projects that contribute significantly to the national grid. Large solar farms, such as those located in desert areas, generate vast amounts of electricity, supporting the country’s energy needs and contributing to its renewable energy targets. These projects demonstrate the scalability and efficiency of solar technology in addressing energy demands on a national level.
4. Future Prospects and Challenges
As the UAE continues to expand its solar energy initiatives, several factors will influence the future of solar panels in the region.
4.1. Innovations and Research
Ongoing research and development in solar technology are expected to drive further advancements. Emerging technologies, such as solar thermal energy and integrated solar solutions, hold promise for enhancing efficiency and expanding applications. Continued investment in research will play a crucial role in optimizing solar panel performance and reducing costs.
4.2. Grid Integration and Storage Solutions
Integrating solar energy into the national grid presents challenges related to energy storage and grid stability. Advances in energy storage solutions, such as high-capacity batteries, are essential for managing the intermittent nature of solar power. The development of smart grid technologies and energy management systems will also contribute to effective grid integration and reliable power distribution.
4.3. Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
The expansion of solar panel installations must consider environmental impacts and regulatory requirements. Ensuring sustainable land use and minimizing ecological disruption are important factors in the planning and execution of solar projects. Regulatory frameworks that support solar energy development and address potential challenges will be crucial for maintaining a balanced approach to growth.
Conclusion
Solar panels represent a beacon of hope for a sustainable energy future in the UAE. Their benefits extend beyond environmental gains to include economic advantages and enhanced energy security. As the UAE continues to invest in solar technology and expand its applications, the potential for solar energy to transform the country’s energy landscape is immense. Embracing innovation, addressing challenges, and fostering collaboration will pave the way for a brighter, cleaner, and more sustainable energy future in the UAE.